堆的概念
属性
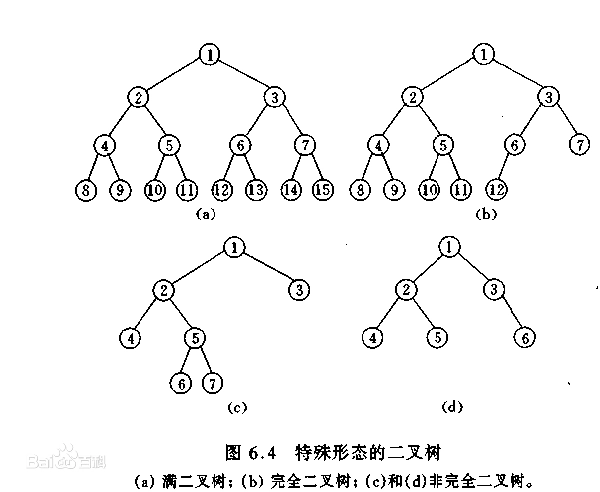
堆是一颗完全二叉树(complete binary tree)。这个前提非常重要,记住这一点才能理解父子结点的索引值关系以及判断叶子结点的原理。
注意:分清完全二叉树和满二叉树。对于满二叉树,国内外定义不同(本文跟随国际定义):
- 国内,仅下图(a)才能叫做满二叉树,满二叉树是完全二叉树的特殊形态。满二叉树必定是完全二叉树;反之不一定。
- 国际,下图(a)与下图(c)都叫”full binary tree”,即一个结点的子结点数要么是 0 要么是 2。满二叉树不一定是完全二叉树,反之也不一定。
分类
分类依据:堆顶元素 & 父子大小关系。
- 大顶堆
- 小顶堆,比如上图(b)
顾名思义,大顶堆就是堆顶是堆的最大值,父结点与子结点关系是父的结点值大于子结点值;小顶堆正相反,堆顶是堆的最小值,父小于子。
堆的操作
备注:
this.size指当前堆的结点总数。
选 0-based 还是 1-based?
首先,先理清一个疑问:根结点应该放在 heap[0] 还是 heap[1] ?似乎有一种观点认为,把根节点放在 heap[1] 能够稍微优化运算速度。
从下标 1 开始实现堆是否是公认的更高效做法?我谷歌后搜索到这个回答stackoverflow: Why in a heap implemented by array the index 0 is left unused?,最高赞答案的观点是:1-based 并不更高效。
查了下 Java 的优先队列源码,它是从下标 0 开始的。
本篇笔记根据《数据结构与算法分析(第三版)》教材示例,选择从 heap[0] 开始存储。
获得父/左子/右子结点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
leftChild(pos) {
return 2 * pos + 1;
// 如果从下标 1 开始存储,则为 2 * pos
}
rightChild(pos) {
return 2 * pos + 2;
// 如果从下标 1 开始存储,则为 2 * pos + 1
}
parent(pos) {
return Math.floor((pos - 1) / 2);
// 如果从下标 1 开始存储,则为 pos / 2
}
判断是否为叶子结点
1
2
3
isLeaf(pos) {
return pos >= Math.floor(this.size / 2) && pos < this.size;
}
为什么这样判断叶子结点?
观察上图(b)可看出,非叶子结点与叶子结点的索引之间有一个明确的分界,假设以索引 x 为分界,可分为两个集合:[0, x], [x-1, n-1],前者为非叶子,后者为叶子结点。因此,只需要找到最后一个非叶子结点 x,就可以获得叶子结点的索引区间,通过判断是否在这个区间内来确定结点是否为叶子结点。
注意:叶子结点不等于最后一层结点!最后一层结点一定是叶子结点,反之不对。比如上图(b)中,结点 7 虽然不在最后一层,但它仍然是叶子结点。
由此问题变为了:怎样找到最后一个非叶子结点?再次观察上图(b),最后一个非叶子结点是 6,它正好是整棵树的最后一个结点的父结点。这并不是巧合,确定最后一个非叶子结点下标的方法就是:找到最后一个结点的父结点。
最后一个结点的下标为this.size - 1,它的父结点根据 2.1 的公式可得:(this.size - 1 - 1) // 2,即(this.size - 2) // 2) = this.size // 2 - 1。由此,最后一个非叶子结点的下标为:this.size // 2 - 1,那么第一个叶子结点的下标自然就能推得:this.size // 2,只要结点下标大于等于这个值,就说明该结点为叶子结点。
备注:两个斜杠
//表示除法结果向下取整
另一种理解方式:
因为堆是一颗完全二叉树,除了最后一层,其他层全满。在完全二叉树中,叶子结点的总数占整棵树结点总数的一半。如果结点总数为奇数,则叶子结点总数比非叶子多 1 个。
假设结点总数为n,则:
- 非叶子结点总数:
n//2,非叶子区间[0, n//2)=> 因此,第一个叶子结点的下标:n//2 - 叶子结点总数:
n-n//2
堆化
本节包含的两个函数,heapifyUp 和 heapifyDown 是堆其他重要操作(插入、删除、建堆)的基础工具。
比较大小
小顶堆:a > b,true。前大于后
大顶堆:a < b,true。前小于后
结点往上层移动【上浮】
其实就是 pos 所在的结点按照小顶堆/大顶堆的结点属性往上移动到该在的位置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/**
* 时间复杂度 o(logn)
* @param {*} pos 要往上移动的结点下标
*/
heapifyUp(pos) {
let parent = this.parent(pos); // 获得pos的父结点下标
// 当pos还没到顶 && pos的父结点值大于【小顶】/小于【大顶】pos值时,pos与父结点交换
while (pos && this.compareItems(this.heap[parent], this.heap[pos])) {
// pos与当前父结点交换
[this.heap[pos], this.heap[parent]] = [this.heap[parent], this.heap[pos]];
pos = parent;
// 获得交换后pos的新父结点
parent = this.parent(pos);
}
}
while 循环中止条件:pos 上浮到了根结点位置 或 pos 的父结点值小于【小顶】/大于【大顶】pos 自身的值
结点往下层移动【下沉】
下沉比上浮略复杂,因为上浮只需要比较当前结点与其父结点;而下沉需要比较当前结点和其两个子结点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
/**
* 时间复杂度: o(logn)
* @param {*} pos 待移动的结点下标
*/
heapifyDown(pos) {
// 已经是叶子结点了,不必继续向下
if (this.isLeaf(pos)) return;
// 获得当前结点的左右子结点下标
let left = this.leftChild(pos),
right = this.rightChild(pos),
temp = 0; // temp为当前结点下一个要移动到的位置(左子结点或右子结点)
// 移到最底就退出
while (!this.isLeaf(pos)) {
// 确定左右子结点之间的大小关系,进而确定pos更可能移动到哪边
// 比如小顶堆,当前结点更可能移动到左右子结点中更小的那边
if (right < this.size) { // 如果有右子结点,那么比较左右大小
temp = this.compareItems(this.heap[left], this.heap[right])
? right
: left;
} else temp = left; // 如果没有右子结点,那么默认左子结点
// 以下代码确认当前结点是否要移动到temp位置
// 如果当前结点比 temp 大【小顶】/小【大顶】,则下沉;
if (this.compareItems(this.heap[pos], this.heap[temp])) {
[this.heap[pos], this.heap[temp]] = [this.heap[temp], this.heap[pos]];
pos = temp;
left = this.leftChild(pos);
right = this.rightChild(pos);
} else break; // 不能移动到temp,则退出
}
}
时间复杂度均为 o(logn) 的原因
堆是完全二叉树,而二叉树的特性就是每个结点最多有两个子结点,因此每棵二叉树每层的结点数公式为:第 i 层结点数 = 2^i(i = 0, 1, ......)。
heapifyUp和heapifyDown都是在层与层之间移动,并且每层最多只停留一次(想象为下楼梯),也就是说无论往上还是往下,最多移动的步数为二叉树的高度,即logn,此对数以 2 为底。
树高与结点数 n 之间的关系?假设树总共有n个结点,且是完全满二叉树(除叶子结点,每个结点都有两个子结点;并且最后一层叶子结点层是满的)。假设树高为 k,则有0 ~ k-1层,树结点总数为 = 2^0 + 2^1 + ... + 2^(k-1) = 2^k - 1 = n,移项取对数得k = log(n+1)。
也就是说,heapifyUp和heapifyDown最多就是从顶层移动到底层,走log(n)步,因此时间复杂度均为 o(logn)。
删除结点
- 删除根结点
1
2
3
removeTop() {
return this.remove(0);
}
直接让最末尾结点(最后一个叶子结点)覆盖根结点,然后让它heapifyDown到自己该到的位置(相当于重整堆)。
- 删除指定位置
pos结点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
remove(pos) {
if (pos < this.size) {
let last = this.getLast();
let delNode = this.heap[pos];
this.size--;
// 如果pos恰好是最末尾结点,那么直接修改size就可以了,否则要进行重整
// if上一句代码已经this.size--了,所以判断是否末尾无需再减1
if (pos < this.size) {
this.heap[pos] = last; // 用最末尾结点的值覆盖待删结点的位置
this.heapifyDown(pos);
}
return delNode;
}
}
如果是非最末尾结点,则用最末尾结点覆盖 pos 结点,然后 heapifyDown;
如果是最末尾结点,则直接删掉。
插入结点
1
2
3
4
5
insert(val) {
let pos = this.size++;
this.heap[pos] = val;
this.heapifyUp(pos);
}
首先增加堆的结点数,新堆的最末尾结点的下标恰好是插入前的堆的总结点数;
然后把新值先放到最末尾结点下标处,最后 heapifyUp,使其移动到自己该呆的位置。
建堆
备注:区分“建堆”和“堆化”。前者是
buildHeap,后者是heapifyUp & heapifyDown;前者是结点之间交换来交换去,后者是结点在层与层之间跨步;前者时间复杂度为 o(n),后者为 o(logn)。
方法 1: 从下到上建堆
备注:此方法好理解,但不常用,效率低。
遍历数组,数组元素按顺序插入堆中。
由于堆的插入操作是将新元素放到末尾,然后逐级向上 heapifyUp,所以是从下到上建堆。
1
2
3
4
5
buildHeap(heap){
for (let i = 0; i < heap.length; i++){
this.insert(heap[i]);
}
}
方法 2:从上到下建堆【常用】
从最后一个非叶子结点开始,将其向下 heapifyDown。因为叶子结点没有可以向下比较的结点了,它们在非叶子结点比较的过程中会参与比较,所以可以剩去一半的比较操作(叶子结点占全部结点的一半)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
buildHeap(){
// 2.2节中有解释最后一个非叶子结点的下标位置公式是怎么得来的:last_non_leaf=size//2-1
for (let i = Math.floor(this.size / 2) - 1; i >= 0; i--){
this.heapifyDown(i);
}
}
建堆的时间复杂度 o(n)
时间复杂度的推导直接看这篇博文。
注意:如何理解上文推导公式中 S 与 S1 与 S2 的关系? S2 是 S1 的公式两边同乘 2得到的,
S2 = 2S1,因此S = S2 - S1 = 2S1 - S1 = S1即S = S1
小、大顶堆的代码区别:如何合并实现?
区别主要在当前结点与其父或子结点比较时的比较函数,体现在代码中即比较函数compareItems()。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
/**
* 比较两数大小关系
* @returns 小顶堆n1 > n2 true;大顶堆n1 < n2 true
* 当n1 == n2,无论大顶或小顶堆都会返回false,结点会停止移动,符合要求
*/
compareItems(n1, n2) {
return this.compare(n1, n2) > 0;
}
this.compare函数在创建对象时由构造函数初始化:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
/**
* 如果输入的不是空数组,则new时自动建堆
* @param {*} heap 数组
* @param {*} compareFunc 比较函数。默认为小顶堆,如果想要大顶需要输入(x,y)=>y-x
*/
constructor(compareFunc = (x, y) => x - y, heap = []) {
this.heap = heap;
this.size = heap.length;
this.compare = compareFunc;
this.buildHeap();
}
抽象出比较函数,小顶堆和大顶堆就可以合并实现为一个类(完整代码见下面第 4 节)。
完整代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
/**
* Heap类Javascript版实现
* 默认小顶堆,在new时输入(x,y)=>y-x后创建的即是大顶堆
*/
class Heap {
/**
* 如果输入的不是空数组,则new时自动建堆
* @param {*} compareFunc 比较函数。默认为小顶堆,如果想要大顶需要输入(x,y)=>y-x
* @param {*} heap 数组
*/
constructor(compareFunc = (x, y) => x - y, heap = []) {
this.heap = heap;
this.size = heap.length;
this.compare = compareFunc;
this.buildHeap();
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size === 0;
}
/**
* 获得堆顶结点的值
*/
getTop() {
return this.size > 0 ? this.heap[0] : undefined;
}
/**
* 获得堆最末尾结点的值
*/
getLast() {
return this.size > 0 ? this.heap[this.size - 1] : undefined;
}
print() {
console.log(this.heap.slice(0, this.size));
}
isLeaf(pos) {
return pos >= Math.floor(this.size / 2) && pos < this.size;
}
leftChild(pos) {
return 2 * pos + 1;
}
rightChild(pos) {
return 2 * pos + 2;
}
parent(pos) {
return (pos - 1) >> 1;
}
/**
* 比较两数大小关系
* @param {*} n1
* @param {*} n2
* @returns 小顶堆n1 > n2 true;大顶堆n1 < n2 true
*/
compareItems(n1, n2) {
return this.compare(n1, n2) > 0;
}
/**
* 堆内插入新元素,先放到堆尾,然后结点向上移动
* 时间复杂度 o(logn)
* @param {*} pos 要往上移动的结点下标
*/
heapifyUp(pos) {
let parent = this.parent(pos);
// 当pos还没到顶 && pos的父结点值大于/小于pos值时,pos与父结点交换
while (pos && this.compareItems(this.heap[parent], this.heap[pos])) {
// pos与当前父结点交换
[this.heap[pos], this.heap[parent]] = [
this.heap[parent],
this.heap[pos],
];
pos = parent;
// 获得交换后pos的新父结点
parent = this.parent(pos);
}
}
/**
* 当堆顶元素被取走后,需要重整堆内元素
* 将末尾元素移到堆顶,然后逐级下降直到满足堆的性质条件
* 时间复杂度: o(logn)
* @param {*} pos
*/
heapifyDown(pos) {
// 已经是叶子结点了,不必继续向下
if (this.isLeaf(pos)) return;
let left = this.leftChild(pos),
right = this.rightChild(pos),
temp = 0;
while (!this.isLeaf(pos)) {
// 先假设左子结点为 temp
temp = left;
// 如果右子结点存在,且值小于左子结点
if (
right < this.size &&
this.compareItems(this.heap[temp], this.heap[right])
) {
temp = right;
}
// 如果pos大于自己子结点中更小的,那么就往下,否则结束
if (this.compareItems(this.heap[pos], this.heap[temp])) {
[this.heap[pos], this.heap[temp]] = [
this.heap[temp],
this.heap[pos],
];
pos = temp;
left = this.leftChild(pos);
right = this.rightChild(pos);
} else break;
}
}
/**
* 从下到上建堆,直接由一个数组原地建堆
*/
buildHeap() {
for (let i = (this.size >> 1) - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
this.heapifyDown(i);
}
}
/**
* 插入新结点,放到堆末尾,然后逐级上升
* @param {*} val
*/
insert(val) {
let pos = this.size++;
this.heap[pos] = val;
this.heapifyUp(pos);
}
removeTop() {
return this.remove(0);
}
/**
* 删除指定位置的结点
* @param {*} pos
* @returns 删除结点的值;若输入pos不在堆中,则返回undefined
*/
remove(pos) {
if (pos < this.size) {
let last = this.getLast();
let delNode = this.heap[pos];
this.size--;
// 如果pos恰好是最末尾结点,那么直接修改size就可以了,否则要进行重整
// if上一句代码已经this.size--了,所以判断是否末尾无需再减1
if (pos < this.size) {
this.heap[pos] = last; // 用最末尾结点的值覆盖待删结点的位置
this.heapifyDown(pos);
}
return delNode;
}
}
}
面试快速手写堆
以下代码用于面试时手写堆,熟练后能做到 5 分钟内写完。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
class Heap {
constructor(func) {
this.h = [];
this.size = 0;
this.func = func;
}
comp(a, b) {
return this.func(this.h[a], this.h[b]) > 0;
}
swap(a, b) {
[this.h[a], this.h[b]] = [this.h[b], this.h[a]];
}
/**
* 下面三个函数可略过,直接在主函数内写公式
*/
left(p) {
return p * 2 + 1;
}
right(p) {
return p * 2 + 2;
}
parent(p) {
return (p - 1) >> 1;
}
/**
* 以上三个函数可略过,直接在主函数内写公式
*/
isLeaf(p) {
return p >= this.size >> 1 && p < this.size;
}
swim(p) {
let parent = this.parent(p);
while (p > 0 && this.comp(parent, p)) {
this.swap(p, parent);
p = parent;
parent = this.parent(p);
}
}
sink(p) {
while (!this.isLeaf(p)) {
let l = this.left(p),
r = this.right(p),
next = l;
if (r < this.size && this.comp(next, r)) next = r;
if (this.comp(p, next)) {
this.swap(next, p);
p = next;
} else break;
}
}
insert(val) {
this.h[this.size++] = val;
this.swim(this.size - 1);
}
removeTop() {
let top = this.h[0];
this.swap(0, this.size - 1);
this.size--;
if (this.size > 0) this.sink(0);
return top;
}
}