模版方法模式确定算法的基本步骤/执行架构,由子类为其中一个或多个步骤填充细节。
模版方法模式满足「支持扩展,拒绝修改(open to expansion, closed to modification)」的开闭设计原则。i.e. 在不修改任何源码的情况下,扩展项目功能。
问题场景
youtube up 主用设计海报作为例子讲解。
设计海报可以遵循一个基本流程:首先设计海报的架构,比如哪里写标题,哪里是视觉中心;之后再根据甲方要求放上标题、图片等。
代码实现
模版中主要包含两种 operations:primitive operations & hooks.
primitive operations
用海报设计为例。
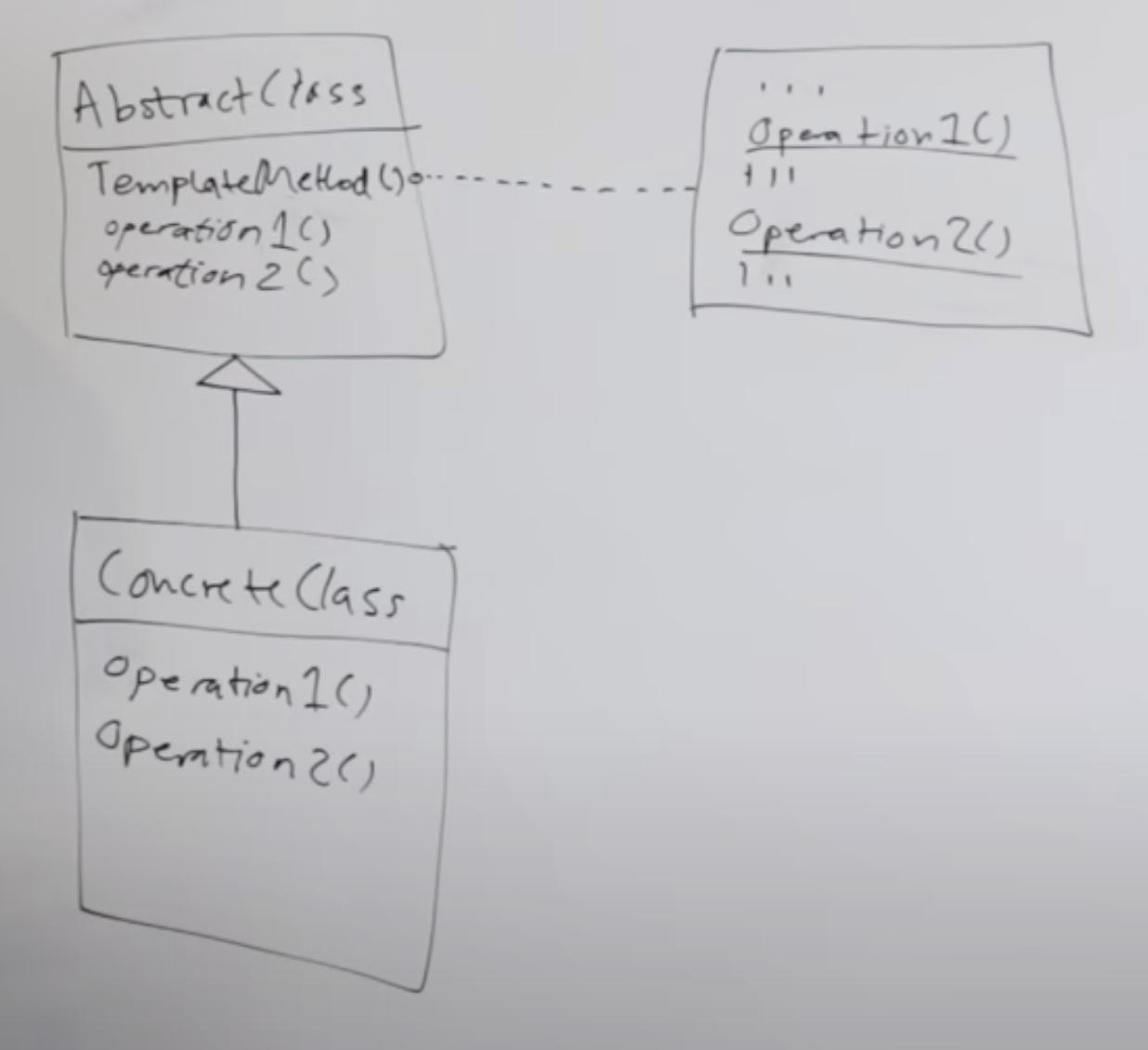 截取自油管视频(链接在“参考资料”)
截取自油管视频(链接在“参考资料”)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
class PosterTemplate {
constructor(titleGenerator, subtitleGenerator, imgGenerator) {
/**
* primitive operations
* which are abstract methods that
* must be implemented by subclasses
*/
this.addTitle = titleGenerator;
this.addSubtitle = subtitleGenerator;
this.addImg = imgGenerator;
}
// template method
generatePoster() {
console.log('==============================');
this.addTitle();
console.log('------------------------------');
this.addSubtitle();
console.log('==============================');
this.addImg();
}
}
function titleForBand() {
console.log('The Best Band in the World');
}
function subtitleForBand() {
console.log('Come see us in the weekend!');
}
function imgForBand() {
console.log('Cool image for awesome band');
}
let posterForBand = new PosterTemplate(
titleForBand,
subtitleForBand,
imgForBand
);
posterForBand.generatePoster();
输出:
1
2
3
4
5
6
==============================
The Best Band in the World
------------------------------
Come see us in the weekend!
==============================
Cool image for awesome band
这个例子中的三个 primitive operations,都是「抽象函数」,which means 超类不实现,子类必须实现。相当于 placeholder。
hooks
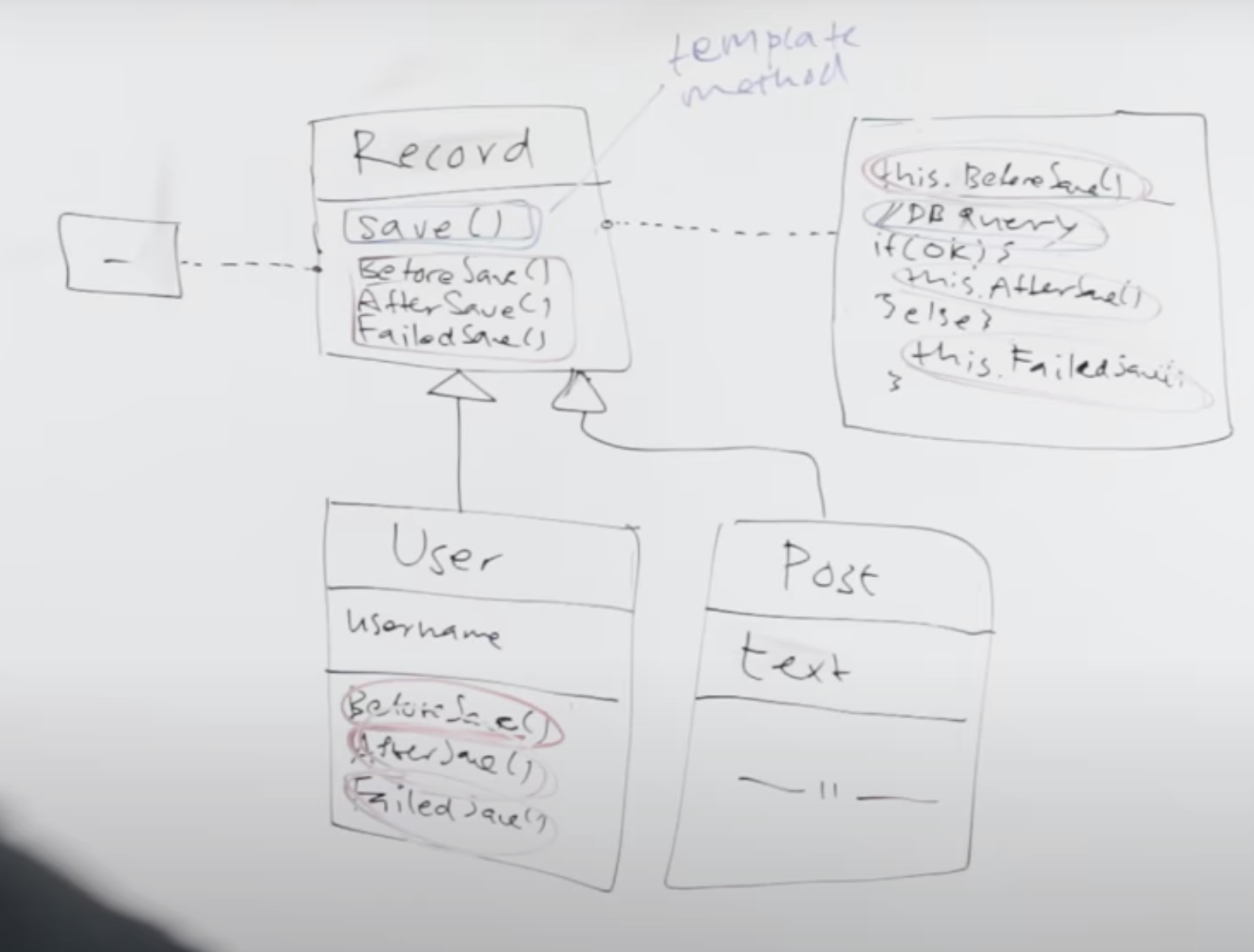 截取自油管视频(链接在“参考资料”)
截取自油管视频(链接在“参考资料”)
youtube up 主用了数据库的例子解释 hooks。(下面的代码把上图中的 save() 换成 validate() 了)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
class Record {
constructor() {}
/**
* template method
*/
validate() {
this.beforeValidate();
// do some data query in database
let res = this.query();
let ok = true; // is query & validation succeed
if (ok) {
this.afterValidate();
} else {
this.failedValidate();
}
}
/**
* primitive operation
* abstract
* must be implemented by subclasses
*/
query(){}
/**
* hooks
* empty but not abstract
* could be override by subclasses
*/
beforeValidate() {
// empty implementation
}
afterValidate() {
// empty implementation
}
failedValidate() {
// empty implementation
}
}
class Post extends Record {
constructor() {
super();
}
query(){
console.log('-> Searching database...');
console.log('-> Results: ...')
}
beforeValidate() {
console.log('Post before validation');
}
afterValidate() {
console.log('Post after validation');
}
failedValidate() {
console.log('Post failed validation');
}
}
let post = new Post();
post.validate();
输出:
1
2
3
4
Post before validation
-> Searching database...
-> Results: ...
Post after validation
primitive operations v.s. hooks
hooks 与 primitive operations 的区别在:
- hooks 不是抽象函数,而是实现为空的空函数。子类重载(override,not implement)hooks。子类可以选择重载 hooks,也可以不重载;
- 对于 primitive operations 来说,子类必须实现它们。
现实应用
- Obsidian 的模版文件。我给设计模式系列笔记设计的模版分为五大块:1)一句话描述;2)问题场景;3)代码实现;4)优缺点;5)现实应用。写笔记的过程就是填充这五大块内容的过程。写笔记可以分为两个步骤:1)写模版/选模版;2)填充模版。
- 框架的基础架构常使用这个设计模式。比如前端框架 vue,
createApp就是 vue 的模版方法,vue 的生命周期函数就是 hooks。 Array.prototype.sort()函数。sort()函数要求我们输入CompareFunction,which 负责比较两个元素的大小。使用sort()时,不需要考虑其具体的实现方式,sort()已经在函数内部规定好了,我们只需要告诉sort()两个元素该如何排序。
与其他设计模式比较
策略模式 > 模版方法模式 > 工厂方法模式。
”>” means 范围广。
v.s. 策略模式
模版方法模式和策略模式都是「封装」方法。
模版方法模式强调「执行流程」。将 operations 按照固定的顺序执行调用。钉死算法的大框架,实现细节由用户自定义。
策略模式强调「策略组合」。策略模式中没有一个必须按照某种顺序执行的框架,它通过抽象出大家共有的行为模式,比如各种各样的鸭子都会飞会叫,它不规定鸭子必须先叫再飞或者先飞再叫。
模版方法模式会指导说,你先做行为 a,再做行为 b,最后做行为 c。你需按照 a->b->c 的行为顺序执行,至于各个行为的具体实现方式则由你定义。
策略模式会指导说,你能做行为 a,也能做行为 b,还能做行为 c。行为 abc 的具体实现方式以及执行顺序均由你定义。
从以上比较可以发现,模版方法模式使用「继承」,而策略模式使用「组合」。还会发现,可以通过策略模式实现模版方法模式,后者是前者的特殊情况。
因此,youtube up 主在视频中建议说,除非你非常确定自己的代码需要一个定死的架构流程,否则应当 favor composition over inheritance, i.e. 选策略模式而不是模版方法模式。
v.s. 工厂方法
工厂方法是模版方法模式的特殊情况。
How?
工厂方法的函数都是「抽象函数」,并且返回值都是「实例对象」。也就是说,工厂方法是只使用 primitive operations 且规定函数返回值的模版方法模式。
参考资料
- Youtube: template method pattern
- 《Head First 设计模式》第八章